ITRex joined the project to
design and build the user interface for the Gen AI assistant and deliver the front-end implementation that integrates into the client’s MES environment. As a result, users can log into the MES and open a window where they can interact with the assistant in GPT style. But this is not a simple agent call; it’s a comprehensive solution that is embedded in all systems and workflows.
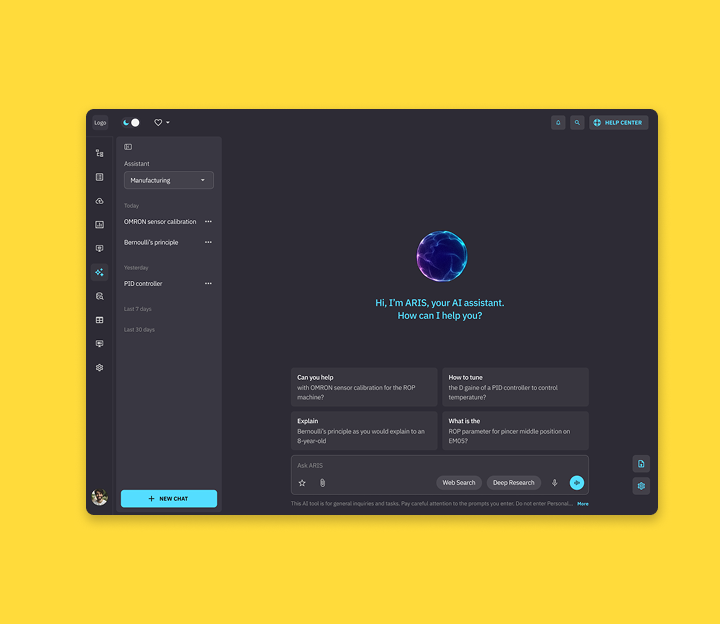
An intuitive UI to interact with the Gen AI-powered MES assistant
The MES assistant supports multiple Gen AI agents (e.g., manufacturing, financial, and language-specific agents such as Spanish and Japanese) that work with different large language models (LLMs). Within the scope of this case study, we focus on the manufacturing agent.
Our interface presents a clean experience where users can:
●
Select the agent and LLM appropriate for the task without understanding the underlying orchestration
●
Define the answer structure for a chatting session. For instance, the user can send a prompt asking the assistant to give concise answers, bullet lists, etc.
●
Save frequently used prompts as favorites
●
Access role-specific FAQs directly inside the chatroom
●
Ask the AI assistant to conduct research and generate reports on a given topic in conversational and podcast formats
Knowledge base & document-driven conversations
We designed UI flows that let employees interact with their company’s knowledge base that we also helped develop.
●
Users with specific access permission can upload PDF documents and images to the knowledge base. Employees can also upload free-form text, but this format is subject to approval. This system enables senior specialists to share their advanced knowledge and make it accessible to their less experienced colleagues.
●
Any employee can query the centralized knowledge base without hunting for physical manuals
●
Employees can upload documents to the chat, making them the topic of the conversation. These documents are removed when the session ends.
Tickets & maintenance workflows that don’t slow people down
We designed collaboration flows between the AI assistant and the maintenance teams:
●
The Gen AI assistant can automatically generate tickets upon noticing an issue on the factory floor
●
Employees can also create and assign tickets in a few clicks
●
The maintenance team can resolve issues either by searching the knowledge base directly or by asking the AI assistant for recommendations. After receiving the initial recommendations, employees can continue troubleshooting via text or voice prompts. The AI always displays references, such as docs, prior tickets, etc., to support its point.
There is a disclaimer stating that the AI assistant can hallucinate and prompting users to verify any given recommendation.
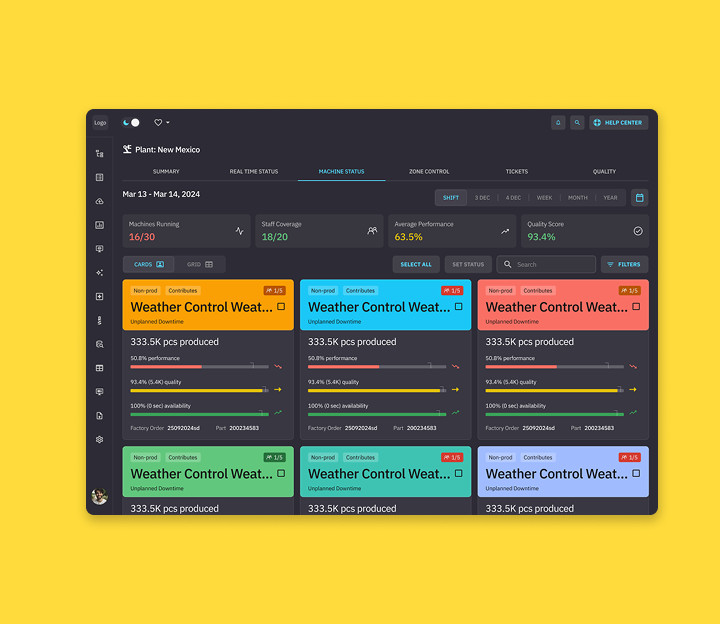
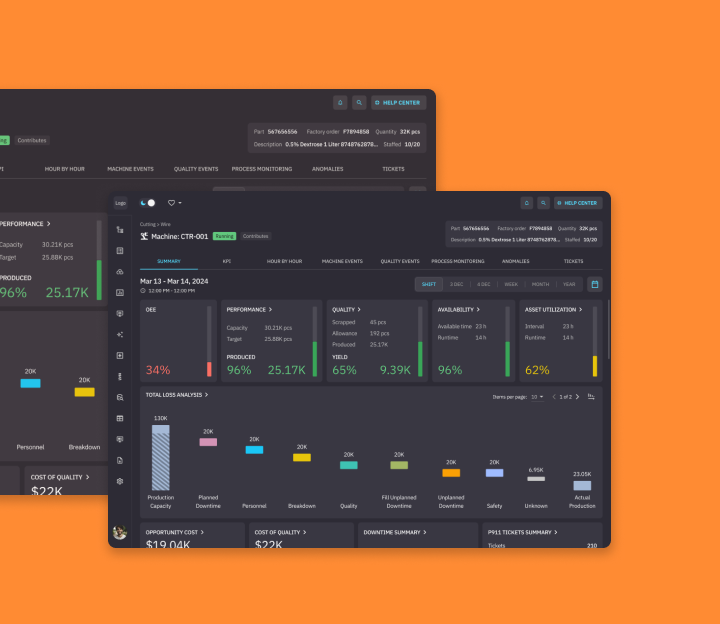
Dashboards made conversational
The UI also supports standardized dashboards displaying statistics on machine performance. Factory managers can ask questions about these stats and their implications in natural language. They can query machine statistics and KPIs and receive structured answers inside the assistant—without switching tools.