What is a smart hospital, and how it works?
Smart hospitals use data and technology to improve their processes and patients’ well-being. They operate in a highly automated and optimized environment. Such medical facilities deploy connected devices, AI, and data analytics. Smart rooms will look differently in each hospital, but they all serve the same goals – improving patient experience, streamlining clinical workflows, and facilitating communication.
Smart hospitals are inspired by the idea that patients are customers, and they expect medical facilities to cater to their needs. As the term “customer” indicates an active and more demanding buyer, intelligent hospitals do their best to offer a unique experience instead of purely focusing on treatments. They even extend their services to patients’ caregivers. For instance, Stanford Hospital retains a health librarian who will help family members find resources to understand the particular diagnosis and prepare to support the patient at their home.
Equipping a hospital with smart wards is pricy. The costs can reach tens of thousands of dollars per room. One listing even mentions a quarter of a million for just one ward.
Digital vs. smart
It is important to mention that digitalization doesn’t make hospitals smart by default. Implementing digital systems, such as robotic process automation in healthcare, is a step towards becoming smart, but it is not the end goal in itself. For example, investing in EHR and abandoning paper-based records doesn’t make a hospital smart, but it is a step in the right direction. Digitalized systems will enable you to capture data. Then you can establish a data strategy and benefit from analytics in healthcare.
How do smart hospitals work?
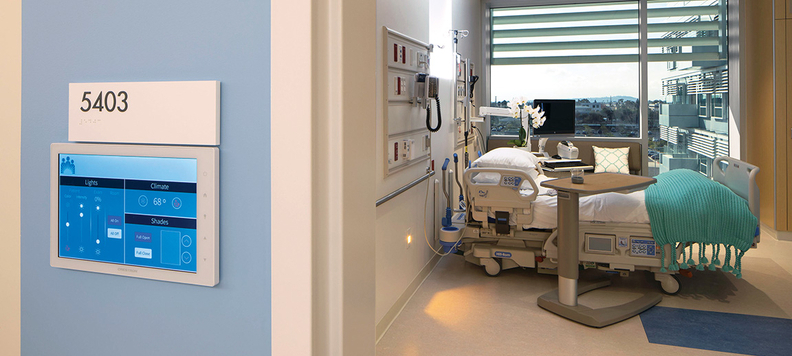
Smart hospitals put data together through complex integrated systems. According to Siemens, “integration begins at the ward level where different systems like lighting, climate control, and shading are combined in one infrastructure (total room automation).”
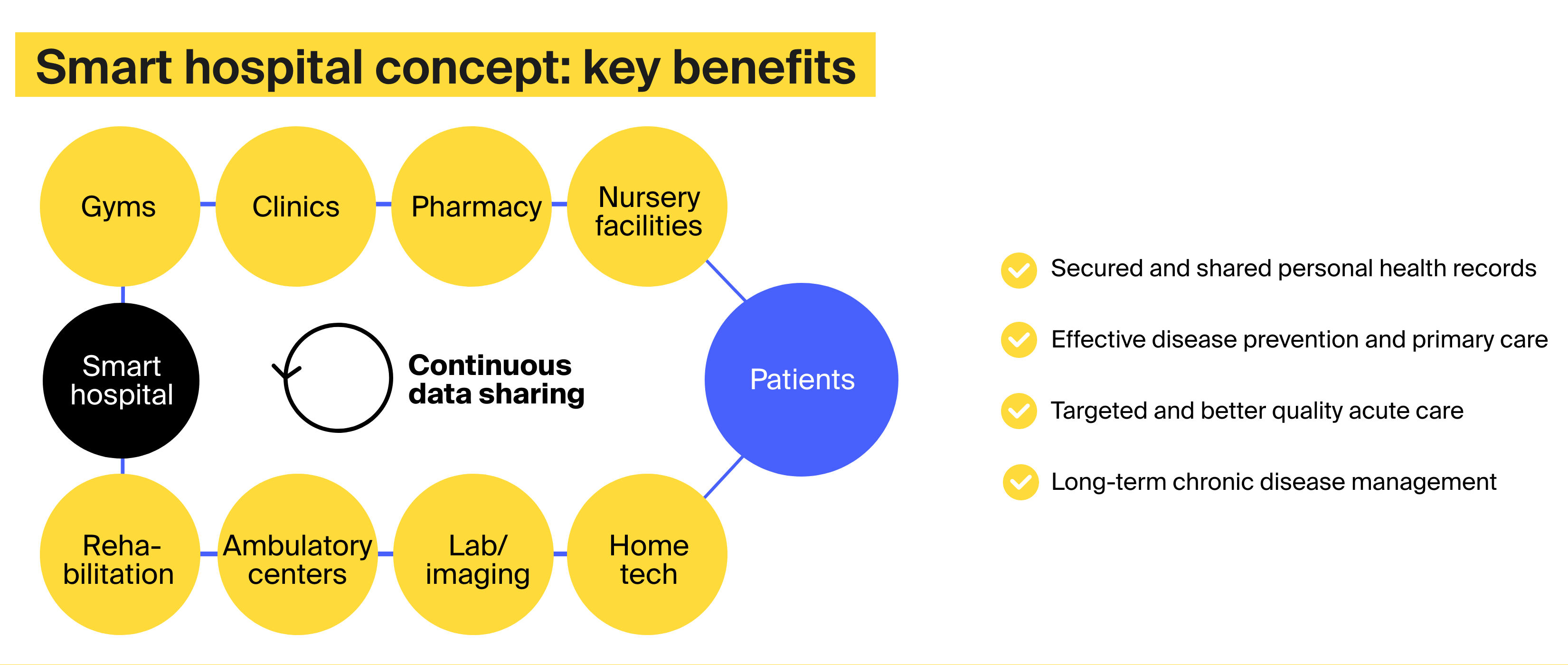
McKinsey views smart hospitals as patient-centric facilities connected to an ecosystem of other organizations and sharing data with them. In such an ecosystem, healthcare management programs are delivered at various locations, including gyms and patients’ homes. Hospitals primarily focus on complex procedures, such as surgeries and intensive care.
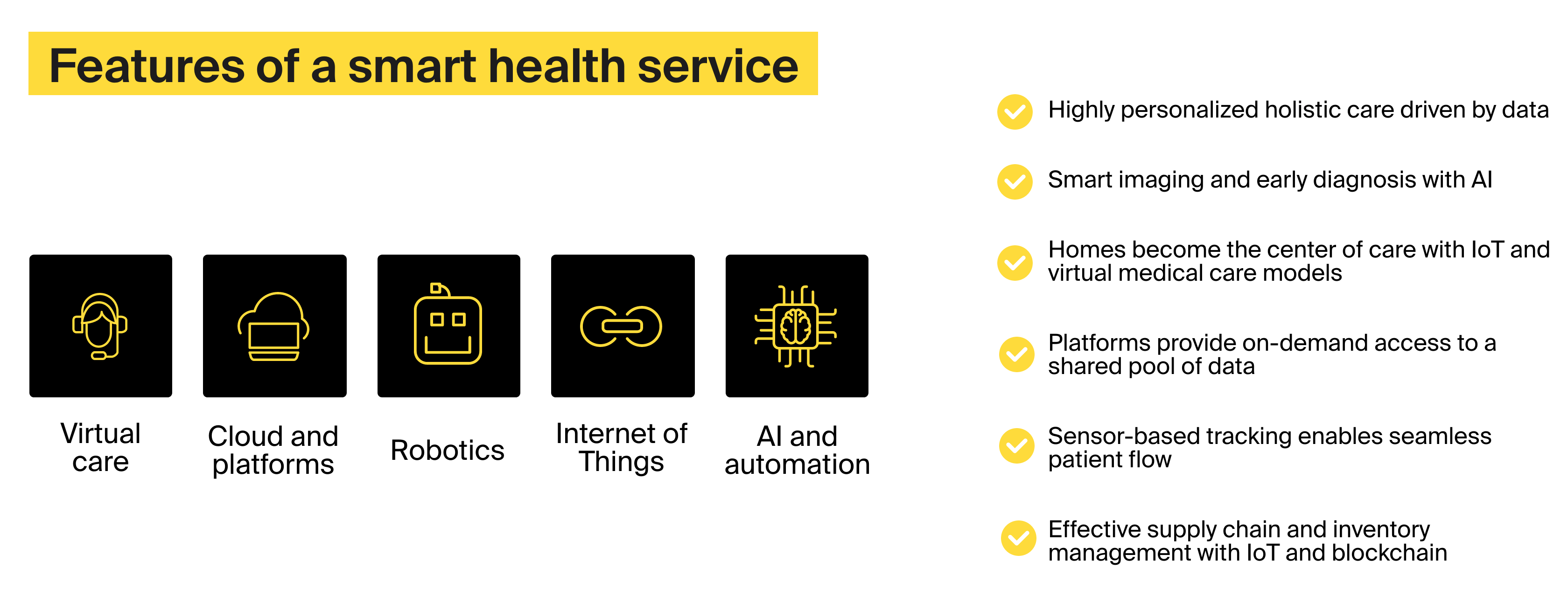
Technology-wise, smart hospitals use the Internet of Things (IoT) and employ a variety of other innovative technologies. This list includes:
-
Artificial intelligence (AI). This technology is often used to detect cancer and other maladies at early stages. AI is also an indispensable part of intelligent automation.
-
Big data analytics. It contributes to disease detection and treatment, facilitates medical research, and manages population health, among other merits.
-
Augmented reality (AR). AR and VR are a powerful tools in pain management, mental health therapy, and medical staff training.
-
The Internet of Bodies (IoB). Medical IoB includes solutions for remote patient monitoring, connected hospital beds that record patients’ vitals, and biometric-powered authentication systems.
-
Cloud platforms. To sustain an intelligent hospital system, you will need to aggregate and analyze large quantities of data. It would be a challenge to accomplish this task fully on premises. And here’s where cloud computing comes in useful.
Smart hospital examples
The Norwegian startup Ably Medical provides an exciting example of a smart bed suitable for senior patients. Ably Bed has embedded sensors to measure patients’ vital signs, weight, and other parameters. It can notify doctors if a patient’s condition begins to deteriorate. The bed’s flexible frame presents another interesting feature. It can adjust automatically to prevent patients from falling or to turn them to alleviate pressure points on their bodies. Ably Bed supports nurses in moving patients around, which can cause injury.
Watch this video to learn more about how this bed was designed and how it helps nurses.
For another inspiration, let’s take a look at the Sunway Medical Center, which won Frost & Sullivan‘s 2021 Malaysia Smart Hospital Company award. This smart center used its technology to adapt well to the pandemic and serve its patients in these difficult times. It has established a connected Telemedicine Command Center that allows remote consultations during the pandemic. Sunway also offers a connected contactless COVID-19 Testing Pod and a vaccination center.
Within its facilities, Sunway is experimenting with innovative technology as well. It has state-of-the-art equipment for radiation treatment for neurological conditions. Its hospital beds are equipped with sensors to monitor patients’ sleep and respiratory rates. On the entertainment side, patients can browse the meal and beverage menu on their smartphones, select options, and place orders in advance.
Smart hospital solutions available on the market
The global smart hospital market is valued at $29 billion in 2021, and it is expected to jump to $59 billion by 2026. Another research suggests that the smart hospital market will already cross the $63 billion mark by 2023. Either way, it’s a promising field, and there are many smart hospital solutions on the market. They can be classified in the following list:
Patient monitoring in smart hospitals
Intelligent hospitals use various patient monitoring solutions both inside the healthcare facility and at the patients’ homes. Here are some examples of smart hospital solutions falling under this category:
-
Displaying relevant patient information at their room entrance: Smart hospitals replace digital banners outside patients’ wards with digital signage. Its display is not limited to the patient’s and the attending physician’s names. Digital signage can connect to the patient’s EHR and project helpful information, such as infections, allergies, and fall risk, among other relevant data. This technology can also introduce visitors to compliance protocols and keep track of people entering the room.
-
Monitoring patients’ vitals: different health tech companies propose their version of monitoring solutions. For example, Thoughtwire built an intelligent hospital system that measures patients’ vitals and alerts the medical staff when someone’s condition is about to deteriorate. BioLert developed a smartwatch and smartphone app based on a patented algorithm to recognize vital information indicating a seizure.
-
Catering to vulnerable patient groups: Millbrae-based Care Coach uses avatar technology to help elderly patients manage their chronic conditions. Doctors and nurses can interact with the users through this avatar, helping them cope without frequent hospital visits.
-
Locating patients: Tan Tock Seng Hospital in Singapore employs a system that monitors patient flow from the moment of admission to discharge. This solution can locate patients around the hospital in real time.
Asset tracking in smart hospitals
Studies show that nurses spend around 40 hours per month searching for lost equipment, and in 16% of the cases, they don’t find what they are looking for and give up. Smart hospitals can supply their equipment with Bluetooth-based iBeacons, RFID, or QR tags and display their real-time location on a dashboard. Such a system can even show which assets are disinfected and are ready to use and which ones are still in preparation mode.
Just recently, the OLVG hospital in the Netherlands teamed up with Philips and the Eindhoven University of Technology to experiment with locating mobile assets. They used location-aware tags and real-time big data analytics. The preliminary results showed that this type of solutions can be successfully used in hospital settings.
Sensors can also be used to locate medical personnel and even ensure that they are following the hospital’s hygiene protocol. For example, Hygenix, Inc employed ITRex to develop an IoT-powered solution, which monitors hospital staff’s hand hygiene practices. Thanks to this solution, the participating hospitals witnessed a 70% increase in hygiene compliance.
Predictive maintenance in intelligent hospitals
Smart hospitals use analytics to detect early signs of failing equipment. Some tools can even predict failure before it actually affects the performance of a device based on changes in its characteristics. Here are a few examples:
-
An Indian startup, CloudPhysician, developed a solution that can catch on early signs of oxygen decrease in intensive care units and transfer this information to a command center where emergency doctors can act immediately and adjust oxygen supply.
-
Saratoga intelligent hospital in New York uses Philips electronic devices to monitor different risks associated with medical hardware. It can report any potential failures before the equipment is out of service.
Smart hospital management systems
A hospital is a complex system, which involves people, equipment, infrastructure, and many different processes. Managing everything manually is an exhausting task. Smart hospitals employ digital solutions to streamline workflows and provide an overview of the facility. Here are some types of tools that help with hospital management:
-
Location-based monitoring: such tools use analytics to identify the most visited hospital areas that often experience bottlenecks and risks of infection and which locations are utilized at half of their capacity. They can also monitor room and hallway cleaning. For instance, Seattle-based Optio3 developed cloud-powered software that aggregates data from hospitals’ smart medical devices and identifies which areas are underutilized and can be more efficient.
-
Building management: a Chinese BOE Hefei Digital Hospital has a hospital management system that connects different operations with the help of IoT. For instance, their patient flow system is linked to the building management hub, allowing heating, lights, and other utilities to turn on automatically just before patient arrival.
-
Smart hospital management software: such solutions enable hospitals to coordinate different operations from one single platform. For example, Sanela Technologies, an Indian health tech startup, designed smart hospital software that serves as one access point for appointments, billing, laboratory reports, etc.
-
Digital twins: this virtual reality-powered technology allows medical facilities to create digital twins to simulate changes and assess alternatives if the hospital wants to expand or optimize space utilization. An Irish startup REIVR uses edge computing and fusion sensors to create 3D digital twins.
Disease diagnosing smart hospital technology
Smart hospitals incorporate applications that help healthcare practitioners to diagnose diseases faster and with higher accuracy. Here are a few examples:
-
Samsung teamed up with KT to offer 5G-driven pathological analysis, vastly accelerating the diagnosing process. Traditionally, the tissue obtained during surgery has to be treated and only then sent to a pathologist. This can take up to 20 minutes. With Samsung’s technology, pathologists can access the necessary data and make their decision faster.
-
A healthcare startup from San Francisco, Freenome, uses AI in genomics to detect and categorize cancer from a blood test. It measures cell-free biomarkers and circulating proteins to spot the disease and identify its type and stage.
Patient entertainment in smart hospitals
Intelligent hospitals are built around the patient and their needs. Such establishments not only focus on their customers’ health, but also want them to feel comfortable during their stay. One example of in-hospital entertainment comes from Cedars-Sinai and BayCare Health System. Both healthcare facilities deployed specialized Amazon Alexa devices, which allow patients to call their relatives and friends, access the TV and radio in hands-free mode, and reach out to their care providers with requests. Using this technology, hospital staff can also communicate with patients informing them about menu changes, games, and podcasts.
Navigation in smart hospitals
Smart healthcare centers employ digital way-finding techniques to help patients and visitors navigate these large establishments with ease. If visitors can’t find their way around the facility, they will be late for appointments and will arrive feeling stressed, which compromises customer experience. Additionally, they may contract infections when wandering into the wrong areas.
The UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital benefits from Pointr’s Deep Location technology to navigate its visitors inside and outside the facility. The solution helps customers find parking spaces, reach their appointment locations, and notify medical staff of their arrival.
What to consider before you begin with smart hospital implementation
Transforming your healthcare facility into an intelligent hospital is a complicated endeavor. In one hospital, smart rooms will look different, as they are designed with a specific patient population in mind. They will use a distinct set of technologies corresponding to the selected patient segment’s needs. Independently of your ward design and the targeted patient group, there are some steps that you can take at the very beginning of your project to increase your chance at success:
-
Establish your vision of a smart hospital
As a first step, it is paramount to understand the unique needs of your healthcare facility. It will be helpful to organize requirements elicitation sessions with different experts from your team, such as doctors, nurses, support staff, etc. You can use focus groups or individual interviews. This will help you uncover the pain points of your employees. For example, if you learn that doctors are wasting too much time locating their colleagues, then location tagging is a must for your intelligent hospital system.
-
Evaluate your existing technology and infrastructure
Analyze your existing legacy systems to understand what can operate as a part of the smart hospital initiative, what needs to be modernized, and what needs to be replaced or is missing. Don’t limit your focus to digital applications. Evaluate your facility’s infrastructure, such as lighting and air conditioning systems, as they are also a part of the prospective smart hospital solution. You can conduct this evaluation together with your selected technology vendor so that they can document the gaps.
-
Resolve integration issues
In the ideal smart hospital environment, all devices are expected to interconnect together. But in our reality, hospital smart devices are produced by different vendors and can’t be properly integrated. Keep this in mind when selecting your machines and applications. If you are beginning your digitalization path, you can choose one particular vendor and stick with them till the end. But if you already have solutions from distinct vendors in place and you want to build on top of that, then you can turn to a vendor-agnostic provider who will build custom solutions that fit your existing system and help connect your heterogenous devices.
-
Think about data interoperability
If your facility doesn’t follow one of the widespread healthcare data interoperability standards, it would be worth investing in one. This will enable you to fit into the interconnected healthcare ecosystem described at the beginning of this article and to team up with other healthcare providers.
-
Invest in cybersecurity
The more connected devices and systems you have, the more vulnerabilities it offers for malicious activities. According to HIPAA Journal, 82% of healthcare organizations have experienced an IoT-induced cyberattack in the past 18 months. You can emphasize the importance of cybersecurity by involving a cyber protection engineer when developing smart hospital use cases.
And here are a few simple steps that you can take to protect your intelligent hospital system:
-
Install timely software updates
-
Protect all devices with strong passwords that are changed frequently
-
Back up your sensitive files on a secondary system
-
Educate employees on your cybersecurity policy
-
Benefit from a virtual private network (VPN) if you need to connect to a network that you don’t trust
-
On a final note
With all their benefits, smart hospitals are a costly investment. However, considering where the healthcare field is headed, passing on smart technologies might cost you even more. Nowadays, patients expect healthcare providers to aggregate and access their data rapidly, whether in health records or medical imaging. They want assistance in hospital navigation, entertainment in their rooms, and fast response from medical staff. Likewise, doctors and nurses are tired of being overwhelmed with manual tasks. They are looking for technology-based assistance, which will be a factor when considering new employment opportunities.
If you are ready to incorporate sensors and connected devices into your environment, it is a good idea to start searching for a reliable IoT healthcare service provider to build your intelligent hospital system. Be sure that the selected vendor can also integrate your existing devices and applications or point you to a reasonable substitute. After all is done, your hospital will be ready to match and even exceed the expectations of both patients and staff members.