What is a healthcare data warehouse?
A healthcare data warehouse serves as a centralized repository for all the healthcare information retrieved from multiple sources like electronic health records (EHR), electronic medical records (EMR), enterprise resource planning systems (ERP), radiology and lab databases, or wearables. The data in the warehouse is transformed to fit unified formatting, so it can be used for analysis with no additional preparation.
A modern data warehouse solution integrates multiple technologies to gather, store, process, and analyze massive amounts of data. These technologies include database management systems like cloud-based Amazon Redshift, Microsoft Azure, and Google BigQuery, or relational database management solutions like Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and IBM Db2. Among other key technologies are ETL tools, data processing engines, APIs, business intelligence tools, and machine learning frameworks.
Healthcare data warehouses are not the only option to store medical data and leverage it for smarter decision-making. Other options include data lakes, which store raw, unstructured, or semi-structured data, and data lakehouses, which combine the flexibility of data lakes with some structure of warehouses.
In contrast to healthcare data warehouses, data lakes and lakehouses do not make information immediately available for reporting and analytics, and they may not be optimized for healthcare-specific applications that require strict regulatory compliance. By organizing data in a structured way, healthcare data warehouses also facilitate efficient integration with medical software solutions, supporting predictive analytics, personalized treatment plans, and operational optimization.
For more information, read our article that explores key differences between data warehouses, data lakes, and data lakehouses.
The healthcare data warehousing market: highlights
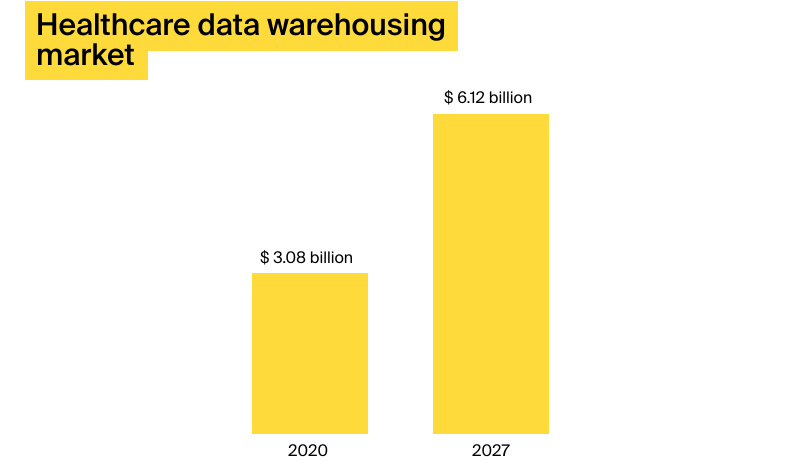
The global healthcare data warehousing market is predicted to grow from $3.08 billion in 2020 to $6.12 billion by 2027 at a CAGR of 10.7%, a study by BlueWave Consulting reports. The increased interest in healthcare data warehousing solutions among industry players can be primarily traced back to:
-
The surge in the volumes of digital data generated by healthcare organizations—about 30% of the world’s data volume is generated by the healthcare sector
-
The broader use of EMR, EHR, and CPOE
-
The more extensive adoption of connected medical devices generating streaming data
-
The call for enhanced operating efficiency brought about by COVID-19
Medical organizations around the globe are thus increasingly investing in healthcare data warehousing solutions. They seek to alleviate the difficulties related to managing the ever-growing amounts of clinical data and reach higher operational efficiency by tapping in predictive analytics, prescriptive analytics, and clinical process automation.
A healthcare data warehouse: value proposition
The value a healthcare data warehouse drives for a medical organization comes from three principal directions:
-
Digitization and automation. With fast access to all kinds of healthcare data, from insurance claims to admission forms to lab test results, healthcare providers optimize and even automate stakeholder journeys.
-
Innovation. Drawing on the capabilities of centralized data storage, healthcare organizations can implement new use cases in the fields of predictive analytics, prescriptive analytics, and the Internet of Medical Things.
-
Achieving strategic objectives. Saving up medics’ time, speeding up healthcare operations, and putting the insights gained with analytics to use, healthcare facilities can improve the quality of healthcare services, reach out to more patients, and expand the range of care delivery options.
Here are a few examples of how medical institutions may leverage a clinical data warehouse and accompanying analytics tools to realize the opportunities above:
-
Clinicians may analyze the data gained from multiple doctors to identify best practices in diagnosing and treating illnesses and chronic conditions. Spotting those doctors whose patients have better outcomes and drilling down to the patient level can help develop more effective treatment protocols.
-
Having all the patient data accessible from one place, doctors may develop more personalized care plans.
-
The transparency of anonymized clinical outcomes may foster collegial collaboration and competition, thus motivating the healthcare staff to deliver high-quality care.
-
Tapping into continuous patient feedback loops can help respond to patients’ needs faster.
-
Clinicians may test the effectiveness of screening methods to enable the shift toward preventive care.
-
Doctors may monitor the population’s health over time to predict epidemics and exacerbations of chronic conditions.
-
Administration may gain insight into how well a healthcare institution performs, develop benchmarks against which the performance can be measured, optimize financial management, and facilitate other administrative operations.
-
Hospitals and other medical institutions can benefit from enhanced reporting opportunities for internal management and external audits, including regulatory compliance checks.
The architecture of a healthcare data warehouse
The architecture of a healthcare data warehouse comprises the following layers:
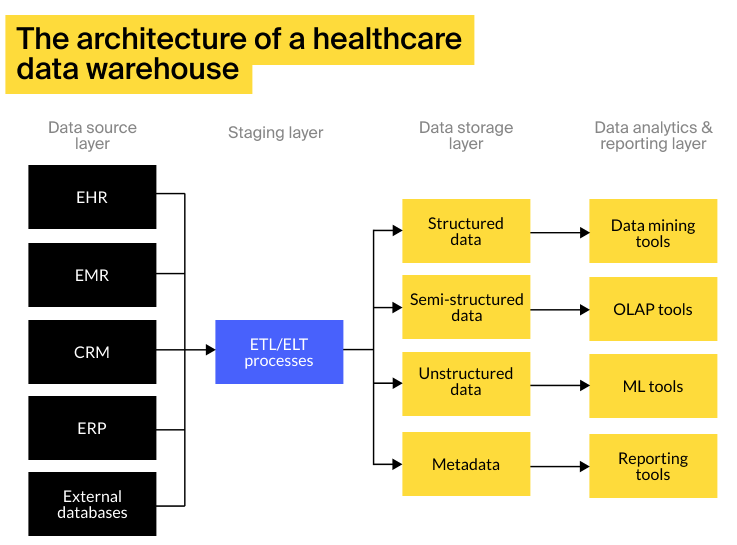
-
Data source layer that consists of clinical, admin, research, precision, patient-generated, and other data from internal and external sources
-
Staging layer that stands for temporary storage, where the data from multiple sources undergoes an extract, transform, load (ETL) or an extract, load, transform (ELT) process and gets combined into a single, consistent body of data.
-
Data storage layer that acts as centralized storage for integrated data. The layer may encompass data related to multiple subject areas or consist of subsets designated to specific areas or departments, known as data marts.
-
Data analytics & reporting layer that comprises data analytics and business intelligence systems for descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, as well as reporting, visualization, and dashboarding tools.
The features of a healthcare data warehouse to prioritize

Data security and compliance
US federal laws, such as HIPAA, and state laws require organizations managing healthcare data to implement security safeguards for protecting personally identifiable information from disclosures and unauthorized use. Trusted ways to ensure data security include:
-
Designing a data management strategy and setting up data governance procedures to secure sensitive information from being accessed by unauthorized people. Data governance can be implemented by creating read-only replicas, setting up custom user groups with pre-defined access rights, or encrypting personally identifiable information.
-
Setting up raw-level permissions to restrict users from viewing specific data entries. Configuring raw-level permissions by account or patient ownership, for example, would give a particular doctor access to their patients’ records, still preventing every doctor from accessing every patient’s personal health information.
-
Setting up permissions at the data analytics and BI level to ensure sensitive data won’t be inappropriately shared through a dashboard or report.
In addition, we recommend performing systematic vulnerability assessments to prevent and timely close any security loopholes.
Data integrity
The data in a warehouse only creates value when it is clear, unambiguous, correct, and transformed to fit an established data model. Data integrity is accomplished through ETL or ELT processes. The critical difference between the two is that with ETL, the data is transformed before reaching the target system, usually at the staging server, while with ELT, the data undergoes transformation once it’s loaded into the warehouse. Depending on the types of healthcare solutions an organization runs on top of a data warehouse, it makes sense to prioritize either ETL or ELT.
-
An ETL engine is easier to implement, and it’s a good fit for use cases with moderate data volumes. However, the process is time-intensive, and the processing time grows together with the data volumes.
-
An ELT engine, in turn, is a suitable option for vast amounts of data. Since raw data is loaded into the target system once, the transformation process is faster, and the processing speed does not depend on the volume of incoming data.
Healthcare data warehouse performance
When it comes to manipulating health-related information, particularly streaming data generated by connected medical devices, glitch-free performance is vital. A healthcare data warehouse can be amplified with the following features to ensure fast and consistent transmission, querying, and retrieval of data:
-
Bitmap indexing that reduces response times of ad hoc queries and boosts data warehouse performance
-
Parallel task execution that allows breaking down complex querying operations into multiple smaller, hence, faster processes
-
Elastic scaling of cloud resources that allows growing or shrinking cloud storage and computing power dynamically in response to workload demands
-
Automated data backups that foster disaster recoveries in case of potential incidents.
Vital integrations to implement
A healthcare data warehouse drives the most value when it serves as a part of a broader ecosystem comprised of the following interoperating components:
-
A data lake. A repository for unstructured and semi-structured data, a data lake may serve as a source of raw data for training machine learning models.
-
Business intelligence. BI solutions may run on the cleansed and structured data stored in the data warehouse, enabling descriptive analytics and supporting decision-making.
-
Machine learning. Bringing ML to healthcare may help realize predictive and prescriptive analytics, fostering diagnosing and treatment and optimizing hospital operations.
A healthcare data warehouse implementation roadmap

The entire healthcare data warehouse implementation process can be broken down into four steps.
-
Planning. This is a crucial step in the whole data warehouse development process, defining all the future efforts. The planning stage deals with assessing the context and thinking over the strategic aspects of adopting a clinical data warehouse. The tasks to carry out include:
-
Define the needs of individuals involved in the data management process and uncover data management bottlenecks or areas of improvement
-
Analyze the available IT infrastructure
-
Formulate the strategic objectives you aim to achieve by implementing a healthcare data warehouse and map those to what you’ve learned
-
Put together a vision of a future healthcare data warehouse and draft an adoption strategy, outlining critical functional and non-functional aspects, including regulatory compliance, security, and performance requirements to a future healthcare data warehousing solution
-
Plan the infrastructure and human resources needed to realize the vision.
-
-
Design. At the design stage, craft the architecture of a future data warehouse, define data integration procedures, think over the healthcare data warehouse model, and plan for the necessary integrations. More specifically,
-
Decide upon a data integration strategy and design the ETL or ELT processes
-
Define the data model:
-
The enterprise-wide data model incorporates the data from multiple subject areas and gives additional opportunities to match up data sets from all organization’s departments
-
The data mart model includes subsets dedicated to specific areas or departments
-
The late-binding data model does not sort data into discrete categories but keeps it freely flowing, allowing data scientists to develop new querying capabilities on the go
-
-
Design data validation procedures
-
Design the necessary integrations
-
-
Development & deployment. The development stage involves rolling out the necessary infrastructure components and coding and implementing healthcare data warehousing software and end-user applications.
-
Ongoing and post-migration testing. Along with ongoing testing activities accompanying development activities, additional validation is needed post-migration. A set of checks are run to validate the migrated data for duplicates, errors, contradictions, or inaccuracies.
On a final note

As more medical organizations initiate healthcare data warehousing projects, it is critical to remember that a data warehouse on its own is not a cure-all. To discover the full value of a clinical data warehouse, it is necessary to develop a thought-out data management strategy aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives and treat a data warehouse as a part of a broader, interoperating analytics ecosystem.
FAQ about data warehousing in healthcare
-
What is the difference between a healthcare data warehouse and an EHR?
An EHR is used to manage and store the personal medical information of each patient while collecting patient data in real time. It is intended for routine clinical use and documentation.
A healthcare data warehouse, in turn, provides an all-encompassing perspective of clinical, financial, and operational information by aggregating data from multiple sources, including EHRs. It is primarily used for analytics, reporting, and strategic decision-making rather than real-time patient care.
-
What are the benefits of data warehousing in healthcare?
When it comes to optimizing your medical business and utilizing all available data, a healthcare data warehouse may prove to be your most useful asset. With the help of centralized data and automated processing, you can easily make educated decisions, maximize resources, and obtain fast, insightful insights. A healthcare data warehouse offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Improved data accessibility. The ease of access to comprehensive and up-to-date data allows for more accurate diagnosing, improves chances of therapy success, and helps develop new treatments.
-
Enhanced data analytics. Analytics gathered from the healthcare data warehouse can support evidence-based care, population health management, and personalized medicine.
-
Operational efficiency. Healthcare data warehousing identifies and optimizes every facet of the medical company because of its solution-oriented analytical capabilities.
-
Exceptional levels of data security and privacy. Advanced security methods are used in data warehousing in healthcare to protect all data from unwanted access.
-
Cost reduction. Analyzing financial data can help with resource management, waste reduction, and better planning and budgeting.
-
-
What are the challenges of implementing a healthcare data warehouse?
The following are some of the major obstacles to putting in place a healthcare data warehouse:
-
Data integration. It can be difficult to integrate data from several systems that have different forms and standards. Standardizing data is necessary to guarantee consistency.
-
Data quality. Inaccurate, partial, or inconsistent data might hinder the effectiveness of analytics and decision-making processes.
-
Security and compliance. Advanced security procedures, such as encryption, access controls, and audits, are necessary to ensure the healthcare data warehouse satisfies stringent security standards and conforms with healthcare legislation (like HIPAA).
-
Cost and complexity. Building and maintaining a healthcare data warehouse requires significant investment in people, software, and infrastructure. Additionally, it calls for knowledge of ETL procedures, database architecture, and data management.
-













